You’ve probably heard people blame their weight on a slow metabolism, but is your metabolism really the culprit? Do you have any control over it, and is it possible to rev up your metabolism to burn more calories?
Metabolism is indeed linked to weight, and while there are health conditions that slow metabolism, such as Cushing’s Syndrome or an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), those cases are rare. So while it may be tempting to blame your metabolism for weight gain, slow metabolism is rarely the root cause of excess weight gain.
What is Metabolism
Metabolism is the process by which your body converts what you eat and drink into energy. During this complex process, calories in food and beverages are combined with oxygen to release the energy your body needs to function.
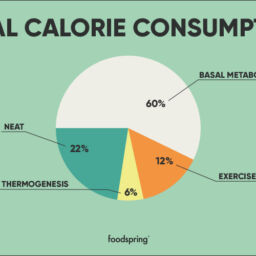
Even when you’re at rest, your body needs energy for all its functions, such as breathing, circulating blood, adjusting hormone levels, and growing and repairing cells. Most often, when we talk about metabolism, we are actually talking about what is known as our basal metabolic rate (BMR). Our BMR is better defined as the number of calories we burn while resting or simply sitting on the couch and watching TV or reading.
Several factors determine your individual basal metabolism, including:
- Your body size and composition. People who are larger or have more muscle burn more calories, even at rest.
- Your sex. Men usually have less body fat and more muscle than women of the same age and weight, which means men burn more calories.
- Your age. As you get older, your muscle amount tends to decrease and fat accounts for more weight, slowing down calorie burning.
How to calculate your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
The most accurate way to determine your basal metabolic rate is to have it measured in a lab. But you also can calculate an approximation of your metabolic rate using an online calculator. Or you can also use the Harris-Benedict Equation:
- Men: BMR = 88.362 + (13.397 x weight in kg) + (4.799 x height in cm) – (5.677 x age in years)
- Women: BMR = 447.593 + (9.247 x weight in kg) + (3.098 x height in cm) – (4.330 x age in years)
Then, after you have your approximate BMR, you can find out your total metabolic rate. But as I will explain shortly, your total metabolism (metabolic rate) is a combination of your BMR and other myriad metabolic processes.
Factors That Can Lower Your Metabolic Rate
Losing weight. The fact is that the smaller your body, the fewer calories it takes to keep it moving. And this effect is amplified if you have lost weight quickly.
Living in a caloric deficit. Restricting calories for more than a few days at a time can also slow your metabolism down.
Losing muscle. Muscle tissue is more metabolically active, meaning the more muscle you have, the more calories you burn than other tissues in your body (such as bone and fat). So if you lose muscle, your metabolism will decrease. Keep in mind, a significant amount of muscle is lost if you lose weight too quickly, so you will have a double whammy on your metabolic rate.
Aging. We all lose muscle as we get older (it’s inevitable), but physically inactive people can lose as much as three to five percent of their muscle mass each decade after the age of 30.
Low thyroid function. If your thyroid gland is not producing enough thyroid hormone, your metabolism can slow down. Conversely, if your thyroid produces too much hormone, your metabolism can go through the roof, but before you get excited, hyperthyroidism is a serious condition, not a great weight loss strategy.
Factors That Boost your Metabolism
Daily movement. Moving more during the day and increasing your overall daily movement is a great way to boost your metabolism. Simple day-to-day tasks such as taking the stairs, carrying groceries, and simply walking more require your body to work harder and burn more calories.
Exercise. The more active, the more calories you burn.
Build muscle. Muscle burns up more calories than fat, so strengthening your muscles will make you into a more metabolically active machine (even when you are sitting on the couch watching tv).
Eat more protein. Protein takes a little more effort for your body to digest than fat or carbohydrate, so increasing the amount of protein in your diet can help you rev the metabolism. Plus, it helps you put on and maintain muscle mass.
Eat enough calories. Too many calories can cause you to gain weight. But eating too few calories can cause your metabolism to slow down. Finding the right balance will support your metabolism without increasing your waist size.
Can Supplements help boost your Metabolism
Beware of products that claim to speed up your metabolism because they are generally more hype than help, and some may cause undesirable or even dangerous side effects. Supplementing with things like hot chilli peppers, minerals, or antioxidants may provide a small boost in your metabolism, but not a significant enough boost to make a difference in your weight. Here are a few others that make big claims but yield minimal results…
Capsaicin it is said that capsaicin can boost your metabolism. But a review of 20 research studies found that capsaicin only increased the number of calories burned by a measly 50 calories per day.
Chromium is a mineral that your body uses in small amounts and is said to help raise metabolism. But a study reported in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that chromium picolinate supplements actually did not affect weight loss.
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) also has mixed results. A review of studies published in the European Journal of Nutrition found that CLA may help with modest weight and fat loss, but the effects were small and uncertain.
And finally, resveratrol was found to burn fat in rats. But the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences found that there is not enough evidence to support its use in humans yet.
It is important to keep in mind that dietary supplement manufacturers in the USA are not required by the Food and Drug Administration to prove that their products are effective before they are sold, so view these products with caution and skepticism.
Ultimately, there’s no easy way to lose weight, and although your metabolism influences your body’s basic energy needs, how much you eat and drink, along with how physically active you are, what ultimately determines your weight. The foundation for weight loss will always be based on physical activity and calorie deficit. But you can help your metabolism stay healthy by using the tips I covered in this article.